Surgery is a fundamental and intricate aspect of medical practice that involves the use of manual and instrumental techniques to investigate, diagnose, and treat various medical conditions or injuries. It is a field that demands precision, knowledge, and skill, as well as a deep understanding of anatomy, physiology, and patient care.
It is a discipline that spans a wide range of specialties, from general surgery to specialized fields like orthopedics, neurosurgery, and cardiovascular surgery. Surgeons play a crucial role in saving lives and improving the quality of life for patients.
Take the following multiple-choice questions to test your knowledge. Best of luck, and remember that the skills you acquire in surgery will be invaluable throughout your medical career.
Acute Abdominal Pain
A 66 year old patient presents with a 1 hour of acute onset central abdominal pain to the A&E department. He has a history of diabetes, stroke, and ischaemic heart disease. He is bed bound in relation to the above co-morbidities. What could be the cause of the central abdominal pain?
- Bowel Obstrudtion
- Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
- Appendicitis
- Pancreattiis
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
Some early blood tests are available and show the following.
Hb 8.6 (13-18 g/dl)
MCV 88 (80-99 fL)
Plt 276 (150-300 x109/l)
WCC 6.2 (4-10 x109/l)
Na 134 (135-145mmol/l)
K 4.3 (3.5-5.1mmol/l)
U 4.3 (4-9mmol/l)
Creatinine 163 (60-100 micromols/l)
CRP 23 (<5mg/l)
Albumin 44 (35-45g/l)
Alk Phos 86 (<110iu/l)
ALT 24 (<40 iu/l)
Bilirubin 16 (<20 micromols/l)
GGT 23 (0-70)
INR 1.0
Glucose 4.5 (mmol/l)
Amylase 36 (<90)
CK 43 (iu/l)
Which one of the following diagnoses are made much less likely in light of these results?
- Bowel Obstrudtion
- Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
- Appendicitis
- Pancreattiis
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
You wish to identify a diagnosis rapidly. Which is the best imaging modality of choice to arrive at a definitive diagnosis?
- Departmental Ultrasound
- Portable Ultrasound
- CT abdomen
- Abdominal Xray
- Laparotomy
Abdominal Pain 2
An 18 year old presents with abdominal pain, vomiting and anorexia for 12 hours. He is found to have generalised abdominal guarding. He has pain more in the right iliac fossa. Palpating in the left iliac fossa is painful but causes more pain in his right iliac fossa.
Blood tests show the following.
Hb 17.5(13-18 g/dl)
MCV 83(80-99 fL)
Plt 216 (150-300 x109/l)
WCC 12.3(4-10 x109/l)
Na132(135-145mmol/l)
K4.5(3.5-5.1mmol/l)
U6(4-9mmol/l)
Creatinine 102(60-100 micromoles/l)
CRP129(<5mg/l)
Albumin 40(35-45g/l)
Alk Phos83(<110iu/l)
ALT 41(<40 iu/l)
Bilirubin 5(<20 micromoles/l)
GGT21 (0-70)
INR 1.1
Glucose 28.1(mmol/l)
Amylase93(<90)
CK43(iu/l)
PSA 2.3(0-4ng/ml)
What is the diagnosis? Please choose as many of the below that apply.
- He is highly likely to have type 1 diabetes
- He is likely to have Munchausen’s
- He is unlikely to have more than one pathology at the same time
- He is likely to have gallstones
- He is likely to have Pancreatitis
- He is likely to have renal colic (Pathology on the left side)
- He is likely to have renal colic (Pathology on the right side)
- He is likely to have food poisoning
- He is highly likely to have appendicitis
ASA status
A 66 year old patient presents with a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm to the A&E department. He has a history of diabetes, stroke, and ischaemic heart disease. He is bed bound in relation to the above co-morbidities. He is found to have an AAA which has ruptured.
Prior to his presentation to hospital what is his ASA classification? (American Society of Anaesthesiologists)
- ASA 1
- ASA 2
- ASA 3
- ASA 4
- ASA 5
C Diff
A 45 year old diabetic man is treated with broad spectrum antibiotics for 2 weeks for an infected foot ulcer.
He subsequently develops diarrhoea which is green, liquid and offensive. He is otherwise well in himself. Which is the diagnostic test of choice to rapidly identify the most likely cause?
- Stool Culture (Microscopy Culture and Sensitivity)
- Stool Culture (Ova Cyts and Parasites)
- Blood Culture
- Stool for Clostridium Difficele Toxin
- Wound Swab
- Stool for PCR
- CT scan abdomen
- MRI scan Abdomen
What is the antibiotic treatment of choice for this patient?
- Metronidazole orally
- Metronidazole IV
- Amoxycillin orally
- Amoxycillin IV
- Tazocin IV
- Cefuroxime IV
- Cefuroxime and metronidazole IV
Diagnostic image
An image taken form a diagnostic test further down the line of this patients care is shown. What is the image on view?
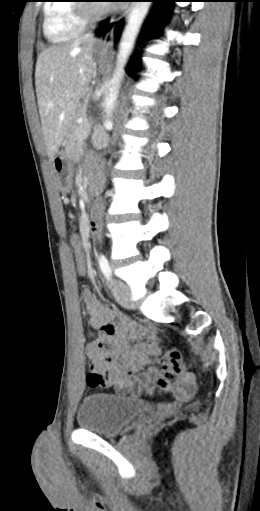
- Lateral X-ray
- MRI Abdomen
- CT Abdomen Axial view
- CT abdomen coronal view
- CT abdomen sagittal view
45 year old diabetic
A 45 year old diabetic presents with a cold blue foot. He has lost sensation. He has no peripheral pulses. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Cellulitis
- Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy
- Acute limb ischaemia
- Chronic peripheral vascular disease and claudication
- Spinal stenosis
- Sciatica
Mortality AAA
For a ruptured AAA what is the estimated mortality in patients prior to presentation in the A&E department?
- <5%
- 10-20%
- 20-30%
- 30-50%
- >50%
Murphy’s test
If a new test has a 70% negative predictive value for cholecystitis, what is the chance a person could still have cholecystitis with a negative test?
- 0%
- 30%
- 50%
- 70%
- 100%
What will the effect of age be on the negative predictive value of Murphy’s sign? (e.g. in a 70 y.o. compared to a 25 y.o.)
- No effect
- Increase sensitivity
- Reduce sensitivity
- None of the above
34 year old female
A 34 year old obese female is known to have gallstones.
At her follow up clinic she complains of intermittent right upper quadrant pain. The pain is there for around 4-5 hours every day. She has a history of Irritable bowel syndrome but has been complaining of increased belching and flatulence.
On examination she has right upper quadrant tenderness but no guarding or rebound tenderness. She is not clinically jaundiced.
Temperature 373
Fingerprick blood glucose 6.2mmol/l
Urinalysis 1+blood 1+ protein
She has had symptoms for the past 12 weeks since a previous admission and feels she “cant take it any more”.
What is the most likely diagnosis here?
- Acute Cholecystitis
- Chronic Cholecystitis
- Cholangitis
- Biliary colic
- None of the above
45 year old
A 45 year old used car salesman presents with a itching and is found to be jaundiced. His Examination is normal other than the finding of jaundice and a palpable gall bladder.
Regarding the following statement (true/false)
He is likely to have gallstones
- True
- False
Perforation
What proportion of patients with a perforated peptic ulcer will have free gas under the diaphragm on an erect CXR?
- 10%
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- >90%
Richters hernia
What is a Richter’s hernia?
- A hernia that is strangulated
- A hernia that involves the small bowel only
- A hernia which is obstructed
- A hernia that is irreducible
- A hernia where only part of the bowel wall circumference herniates
